What Is Factom?
Factom is a blockchain protocol that separates the immutability of blockchain technology from the currencies that are usually associated with it. This makes it easier and cheaper for businesses to store data on the blockchain.
Factom attempts to solve three main problems seen in the Bitcoin network:
- Speed – Bitcoin transactions take at least 10 minutes for a single confirmation. With a community standard of 6 confirmations before a transaction is fully processed, many of them take over an hour.
- Cost – Bitcoin transaction fees have been increasing and may continue to do so as more transactions enter the network.
- Bloat – With 1MB block sizes, the number of possible transactions per second is capped. Even the implementation of Segregated Witness (SegWit) and the Lightning Network may not be enough of an improvement to curb Bitcoin’s scaling issues.
Additionally, the documents and data stored using Factom can easily be audited which further lowers the cost needed for businesses to have a secure and accurate data store.
Factom is particularly useful for businesses in which important data regularly change hands. Documents such as land grants and medical records need to have ensured accuracy as they pass from one person to the next. Storing data on the blockchain provides an immense amount of value to these businesses. Maintaining paper records is expensive and traditional digital storage is vulnerable to malicious tampering. Factom solves both of these issues.
In this Factom guide, we’ll go over:
- How Does Factom Work?
- Factom Team & Progress
- Factom Trading
- Where to Buy FCT
- Where to Store FCT
- Conclusion
- Additional Factom Resources
How Does Factom Work?
Factom uses two tokens on the network:
- Factoids
- Entry Credits
Factoids (FCT)
Factoids have their own chain in Factom and can be traded freely like most other cryptocurrencies. These coins decentralize the system and prevent users from spamming the network.
Factom servers receive Factoids as a reward for maintaining the network. The network releases these rewards at a fixed rate (~73,000 per month) in a process that’s independent of their price.
Entry Credits (ECs)
You can use Factoids to purchase Entry Credits through the protocol. Entry Credits are non-transferable and you can only use them to pay for Entries or to vote for Authority nodes.
Because they have little intrinsic value, you can store Entry Credits in a low-security area with little risk that thieves will steal them.
You need to spend Entry Credits to add data to the Factom blockchain. When you spend an Entry Credit, the Factoids that you used to buy it are removed from the system (AKA burned).
Separating Factoids from Entry Credits opens up Factom to users who either don’t understand or don’t want to use cryptocurrency. They can simply buy Entry Credits using the currency of their choice. Factom then buys Factoids from the open market and burns them to cover the purchase.
The Factom Chain
Each Entry that you submit has a Chain ID. The Chain ID determines which sub-group should include the Entry. Entries have a maximum size of 10KB, but you can use multiple Entries to link together larger files.
A sequence of Entries forms a Chain. The Chain records the order of the Entries which leaves an audit trail. To put it simply, Chains are like folders, and Entries are like the files that you place into folders.
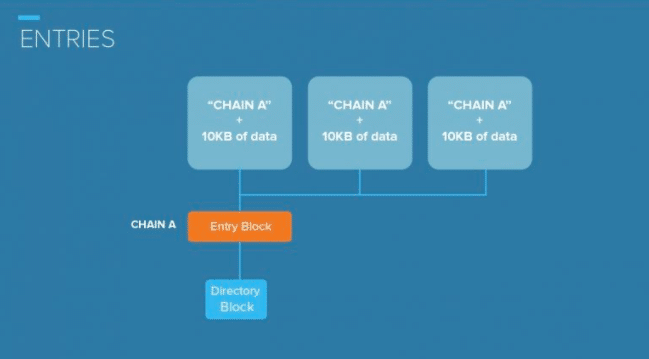
An Entry Block is a group of hashes of all the Entries with a particular Chain ID. It’s important to note that the Entry Block contains just the hashes, not the actual data of the Entries.
Every minute, the Federated Servers create a Directory Block by grouping together the hashes of the Entry Blocks from that timeframe.
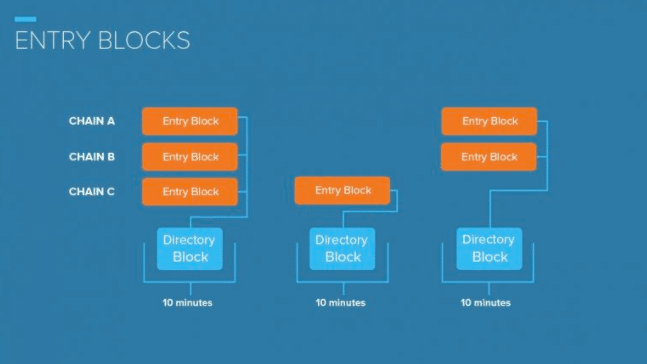
Once 10 Directory Blocks are formed (every 10 minutes), the hashes from those Directory blocks are anchored to the Bitcoin blockchain. The Authority node that performs this action is chosen at random.
The network’s design makes auditing records an easy and low-cost process.
In Bitcoin, you need the entire history of the blockchain to validate a transaction. This isn’t necessary with Factom. Using Directory Blocks and Chain IDs, you can greatly reduce the amount of bandwidth needed to audit the records.
Three Types of Servers
Factom uses a consensus algorithm similar to the Raft algorithm. Using this algorithm, the network reaches consensus by electing a leader randomly from the pool of Federated Servers.
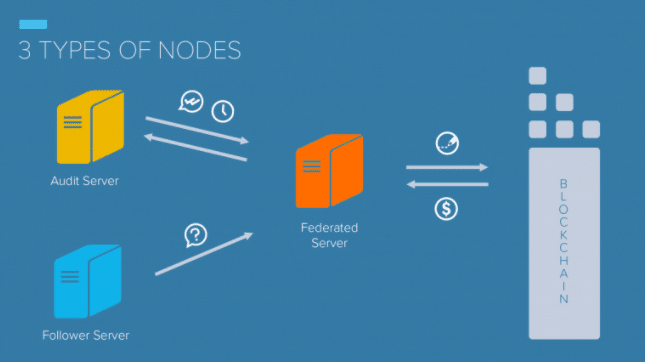
Federated Servers are the primary servers running the Factom network. They are the only ones that can write data to the blockchain and receive Factoid rewards.
These servers send a “heartbeat message” to the followers on the network to prove their existence. If a Federated Server doesn’t produce a heartbeat message, the followers immediately start an election to choose a new Federated Server to take its place.
Audit Servers double-check the work of the Federated Servers. If a Federated Server makes a mistake, it becomes an Audit Server, and one of the Audit Servers upgrades to a Federated Server.
These servers don’t receive rewards for the work that they do.
Follower Servers can only make transaction requests. When they receive an entry request, they forward it on to a Federated Server.
The network doesn’t perform audits on initial Entries, so you should audit all of your Entries before entering them into the system.
[thrive_leads id=’5219′]
Factom Team & Progress
The Factom project began in 2014 which puts it on the older end of the blockchain spectrum. The team has made steady progress since then.
They released the first version of Factom in early 2015 and had their token sale in the middle of that year. In August of 2015, they were accepted into the Plug and Play FinTech accelerator and were chosen as one of Austin’s A-List start-ups in May 2016.
Based out of Austin, TX, the core team has multiple members with several years of experience in the blockchain space.
Paul Snow leads the team as founder and CEO. He also serves as the Chief Architect for the open-source project, DTRules, and founded the Texas Bitcoin Conference.
Blockchain Can Legally Authenticate Evidence, Chinese Judge Rules https://t.co/P7svO2ytzI via @CoinDesk
CoinDesk is downplaying Factom here, but the hashes were in Factom which anchors into Bitcoin. Our people in China helped provide technical support in this case!
— Paul Snow (@paulsnx2) June 29, 2018
Factom currently has over 11 million entries as well as some notable partnerships. The team is working with the Department of Homeland Security to provide audit trails for data collected at the U.S. borders. They’re also working with the Gates Foundation to store medical records for people in developing countries.
In June 2018, a Chinese court used data stored with the Factom blockchain as legal evidence, setting a precedent for future cases.
In May 2018, the Factom team completed the last major milestone of their whitepaper, M3. With the implementation of M3, the authority servers switched from ones operated by Factom, Inc. to independent operators across nine countries. Furthermore, the team made substantial improvements on the blockchain’s speed, increasing throughput by 5x and decreasing confirmation time by a factor of 600. They also added support for Ethereum blockchain anchors.
Competitors
The company has few direct competitors. Its biggest competitor is NEM which released a whitepaper for Apostille in 2017. Like Factom, Apostille specializes in the notarization and timestamping of data and documents.
Factom Trading
The FCT price reached an all-time high (in BTC) of ~$33.72 (~0.0135 BTC) in June 2017. For almost all of the remainder of 2017, the price steadily dropped with a short-lived spike at the end of August. Starting in November 2017, FCT skyrocketed alongside the rest of the market to reach an all-time high (in USD) of around $77.65 (~0.00505 BTC) in January 2018.
Following that bull run, FCT fell throughout most of 2018, hitting a floor of about four bucks. Factom has been one of the few projects to begin to seemingly break out of the 2018 bear market. At the beginning of November, the FCT price started to rise once again to nearly ten dollars and has remained around that price. As this price movement is occurring in a time of poor market sentiment, it could be a sign that Factom is gaining significant adoption among enterprises.
The price of FCT is directly tied to the amount of network usage. As more businesses join the network, it will become more costly to submit Entries which will, in turn, affect the FCT price.
Once the number of FCT being burned outpaces the 73,000 that are created each month, the currency will become deflationary. Passing this breakeven point should drive the price up even further.
Where to Buy FCT
You can purchase FCT on Poloniex, and Bittrex as a trading pair with Bitcoin.
To buy FCT on these exchanges you first need to own Bitcoin or purchase some on another exchange such as GDAX or Gemini. From there, you can transfer your Bitcoin to make the exchange.
CoinMarketCap lists all of the exchanges and trading pairs that are available for Factom.
Where to Store FCT
You have two recommended wallet options to store your FCT:
- Secure (Encrypted) Enterprise Wallet
- Ledger Nano S
The Enterprise Wallet is available on Mac, Windows, and Linux. You can find instructions to download and use the wallet here.
You can also store your FCT on the Ledger Nano S hardware wallet. The Ledger is one of the most trusted and secure wallets in the cryptocurrency community.
They aren’t many other wallets that support FCT yet but they seem to be gaining traction. Exodus’s new wallet, Eden, supports FCT, but it’s still in pre-release, so you may have issues when using it.
Conclusion
Factom is a well-established project that’s solving a huge problem that spans across multiple industries. Although marketing hasn’t been the team’s focus, they’ve been working in the shadows to form business partnerships and continue improving their products.
The team not only has experience working on previous projects together but also share several years of blockchain knowledge.
As the project grows, it’ll be interesting to see how the FCT price responds and what will happen if or when it hits a deflationary point.
Editor’s Note: This article was updated by Steven Buchko on 11.27.2018 to reflect the recent changes of the project.
Additional Factom Resources
Never Miss Another Opportunity! Get hand selected news & info from our Crypto Experts so you can make educated, informed decisions that directly affect your crypto profits. Subscribe to CoinCentral free newsletter now.










